Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Tackling Trigger Points
Posted by Dennis R. Escalera on 2nd Jan 2025
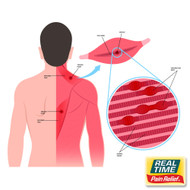
Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is a chronic condition characterized by pain and stiffness in specific muscle groups caused by trigger points—sensitive knots in the muscle that can radiate pain to other areas. Unlike temporary muscle tension, MPS can persist and significantly impact daily activities. This article explores the causes, symptoms, treatments, and the role of topical solutions with nature’s ingredients in managing this complex condition.
Understanding Myofascial Pain Syndrome
MPS is a musculoskeletal disorder involving both muscle and connective tissue (fascia). It is often confused with other pain conditions, but its defining feature is the presence of trigger points. These points are tight bands of muscle that are tender to the touch and can cause referred pain in seemingly unrelated areas.
Causes and Risk Factors
MPS is typically caused by muscle strain or overuse. Contributing factors include:
- Repetitive Strain: Prolonged or repetitive movements, often related to work or sports.
- Injury: Acute muscle trauma can lead to the development of trigger points.
- Poor Posture: Incorrect body alignment can put strain on muscles and fascia.
- Chronic Stress: Emotional tension often manifests physically, contributing to muscle tightness.
Symptoms of MPS
The primary symptoms include:
- Localized Muscle Pain: Often deep, aching, and persistent.
- Trigger Points: Small, firm knots in the muscle that are painful when pressed.
- Referred Pain: Pain radiating from trigger points to other areas of the body.
- Muscle Stiffness and Weakness: Difficulty moving the affected area or maintaining strength.
- Sleep Disturbances: Pain can interfere with restful sleep, further exacerbating fatigue.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing MPS involves:
- Clinical Examination: Identifying trigger points and assessing pain patterns.
- Patient History: Understanding symptoms and potential contributing factors.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Ruling out disorders like fibromyalgia or arthritis.
Treatment Options
MPS treatment focuses on relieving pain, releasing trigger points, and improving muscle function.
- Physical Therapy:
- Trigger Point Release: Techniques like massage, dry needling, or myofascial release to deactivate trigger points.
- Stretching and Strengthening: Exercises to restore flexibility and muscle balance.
- Medications:
- NSAIDs: For temporary relief of inflammation and pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: May be prescribed to reduce muscle tension.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Incorporating ergonomic practices at work.
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Role of Topical Solutions in Managing MPS
Topical creams and lotions can provide targeted relief for MPS symptoms. When formulated with nature’s ingredients, these products offer a non-invasive approach to pain management.
- Key Ingredients in Topical Products:
- Peppermint Oil: Contains menthol, which provides a cooling sensation and may help to soothe muscle pain.
- Camphor: May help to increase blood flow and reduce stiffness.
- Ginger Extract: Offers anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Shea Butter: Moisturizes the skin while acting as a carrier for active ingredients.
Advantages of Topical Applications
- Localized Action: Works directly at the site of pain, avoiding systemic side effects.
- Ease of Application: Simple to use and can be applied multiple times daily, as needed.
- Enhanced Massage Effect: When used during a massage, it can aid in the release of trigger points.
Living with Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Effective management of MPS requires a combination of medical treatments, physical therapy, and self-care strategies. Incorporating topical solutions as part of a comprehensive care plan can provide quick relief and support long-term recovery. Regularly addressing trigger points and maintaining muscle health through exercise and ergonomic practices can help prevent flare-ups.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12054-myofascial-pain-syndrome
- Mayo Clinic. Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myofascial-pain-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20375444
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. More Stretching, Less Stressing. Available at:https://www.nccih.nih.gov/research/blog/more-stretching-less-stressing