Joint Pain Relief for Active Lifestyles: A Natural Approach
Posted by Dennis R. Escalera on 3rd Feb 2025
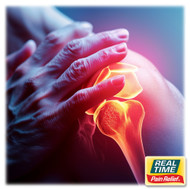
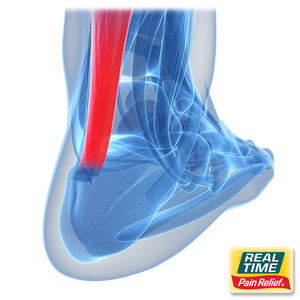
Joint pain can arise from repetitive movements, high-impact activities, or underlying conditions such as arthritis. Staying active while managing joint health is essential for long-term mobility.
How Topical Pain Relief Creams Can Help:
Topical creams can help manage joint pain by delivering pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory ingredients directly to the affected joints.
Key Ingredients That Can Help:
- Glucosamine: Known for supporting cartilage health.
- Chondroitin: Helps maintain joint fluid balance.
- Willow Bark: Contains salicin, a compound similar to aspirin, which may help to reduce pain and swelling.
Other Management Tips:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling
- Proper warm-ups and cool-downs
References: