Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Managing Pain and Stiffness
Posted by Dennis R. Escalera on 2nd Jan 2025
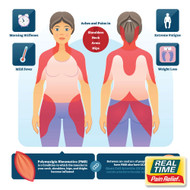
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects older adults, causing widespread pain and stiffness in the shoulders, hips, and other large joints. This condition can have a profound impact on mobility and daily activities. While its exact cause remains unclear, effective management strategies, including topical solutions with nature’s ingredients, can help alleviate discomfort.
Understanding Polymyalgia Rheumatica
PMR is most commonly seen in individuals over 50 years of age, with the risk increasing with age. It affects women more frequently than men and often has a rapid onset. Although the symptoms can be severe, PMR typically responds well to treatment when diagnosed early.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of PMR is unknown, but several factors may contribute:
- Immune System Dysfunction: PMR is believed to be an autoimmune condition, where the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic markers, such as HLA-DR4, may increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Viral infections could potentially act as a trigger.
Symptoms of PMR
PMR is characterized by:
- Pain and Stiffness: Particularly in the shoulders, neck, and hips, often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty performing everyday tasks, such as dressing or reaching overhead.
- Fatigue and Malaise: Generalized tiredness and a sense of being unwell.
- Low-Grade Fever: Occasionally accompanies other symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing PMR involves:
- Clinical History and Examination: Evaluating symptom patterns and physical limitations.
- Blood Tests: Elevated inflammatory markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), support the diagnosis.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: PMR must be differentiated from other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for PMR involves reducing inflammation and managing symptoms to restore function and quality of life.
- Medications:
- Corticosteroids: Low-dose prednisone is the most common and effective treatment. Symptoms often improve within days of starting therapy.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): May help with mild cases or as adjuncts to corticosteroids.
- Physical Therapy: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to improve flexibility and prevent muscle atrophy.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, adequate hydration, and regular exercise are essential.
Role of Topical Solutions in Managing PMR
Topical creams and lotions can provide localized relief from pain and stiffness, complementing systemic treatments. These products are particularly beneficial for managing muscle and joint discomfort in PMR.
- Key Ingredients in Topical Products:
- Menthol: Offers a cooling effect that may help to soothe inflamed areas and distract from pain.
- Eucalyptus Oil: May help to reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties and ability to reduce irritation.
- Boswellia Serrata Extract: Contains compounds that might inhibit inflammatory pathways.
Advantages of Topical Applications
- Targeted Relief: Applied directly to the affected area for precise pain management.
- Minimal Systemic Side Effects: Unlike oral medications, topical products have limited absorption into the bloodstream.
- Ease of Use: Convenient for on-the-go application and can be incorporated into daily routines.
Living with PMR
PMR is a manageable condition with the right approach. Early diagnosis, adherence to medical advice, and adopting supportive therapies, such as topical solutions and physical therapy, can lead to significant improvements in symptoms. Patients are encouraged to maintain open communication with healthcare providers and consider complementary methods, like topical creams, to enhance their quality of life.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/polymyalgia-rheumatica/symptoms-causes/syc-20376539
- Arthritis Foundation. Managing Pain and Stiffness in PMR. Available at: https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/polymyalgia-rheumatica