Exploring Morton's Neuroma
Posted by Dennis R. Escalera on 1st Jun 2024
Introduction
Morton's Neuroma is a common foot condition that affects the nerves between the toes, typically causing pain in the ball of the foot. Often mistaken for a simple irritation or a less serious issue, Morton's Neuroma can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
What is Morton's Neuroma?
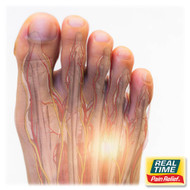
Morton's Neuroma involves the thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to your toes. This condition often develops between the third and fourth toes, resulting in pain, burning sensations, or numbness in the ball of the foot. It is frequently described as feeling like you are standing on a pebble in your shoe.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Morton's Neuroma is not well understood, but several factors contribute to its development. These include wearing high heels or tight shoes that compress the toes, high-impact athletic activities like running that place repetitive stress on the foot, and foot deformities such as bunions, hammertoes, or flat feet.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Morton's Neuroma typically include:
- Pain in the forefoot and between the toes
- Tingling, burning sensations, or numbness in the ball of the foot
- A feeling as if you're standing on a fold or pebble
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Morton's Neuroma usually involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. The doctor may press on the foot to feel for a tender spot or perform tests like an ultrasound or MRI to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Morton's Neuroma focuses on relieving the pressure and inflammation. Non-surgical treatments include:
- Changing footwear to shoes with wider toe boxes or lower heels
- Orthotic devices to provide support and reduce pressure on the nerve
- Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications
In cases where non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options may be considered. These procedures aim to relieve pressure by removing the affected nerve or releasing surrounding tissues.
Nature's Ingredient Topical Pain Relief
Topical pain relief creams and lotions containing nature's ingredients can also be beneficial for managing symptoms associated with Morton's Neuroma. Menthol may temporarily help to reduce pain through its cooling and soothing effects. Other beneficial ingredients include capsaicin, arnica, and peppermint oil. These nature-derived compounds provide a non-invasive treatment option that can be used in conjunction with other therapies to manage pain effectively.
Conclusion
Morton's Neuroma can be a painful and frustrating condition, but with the right approach, it is manageable. Understanding the causes and symptoms, along with a combination of conservative treatments and remedies derived from nature, can help sufferers reduce pain and return to their normal activities.
References
- American Podiatric Medical Association: https://www.apma.org/neuromas
- Mayo Clinic – Morton's Neuroma:https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mortons-neuroma/symptoms-causes/syc-20351935
- Cleveland Clinic – Morton's Neuroma: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15118-mortons-neuroma